The Internet of Things (IoT) and how it’s changing the world at a fast pace and influencing every aspect of our lives is a highly talked subject. In the past 2 decades, we have seen a great technological evolution. Significantly among the Industrial Internet of Things. Conversations about IoT and its implications have become part of the daily background noise and we’re only at the beginning of the journey. Yet if asked, many people don’t actually know what IoT stands for or they only have a vague idea of what it means.
To cut to the chase, IoT refers to physical devices that are connected to each other through the internet, gathering and sharing valuable data. So basically, it’s a complex network of smart objects, combining the physical and the digital worlds together and enabling users to collect information from a variety of sources.
These innovations are creating solutions for the new challenges and possibilities. The IoT has many applications, from smart homes to smart supply chains or even smart cities. However, one of the most discussed subcategories of IoT is probably the industrial internet of things or IIoT. To get a clearer picture of how things work in this area, we must understand how IoT can impact the various industries.
What is IIoT?
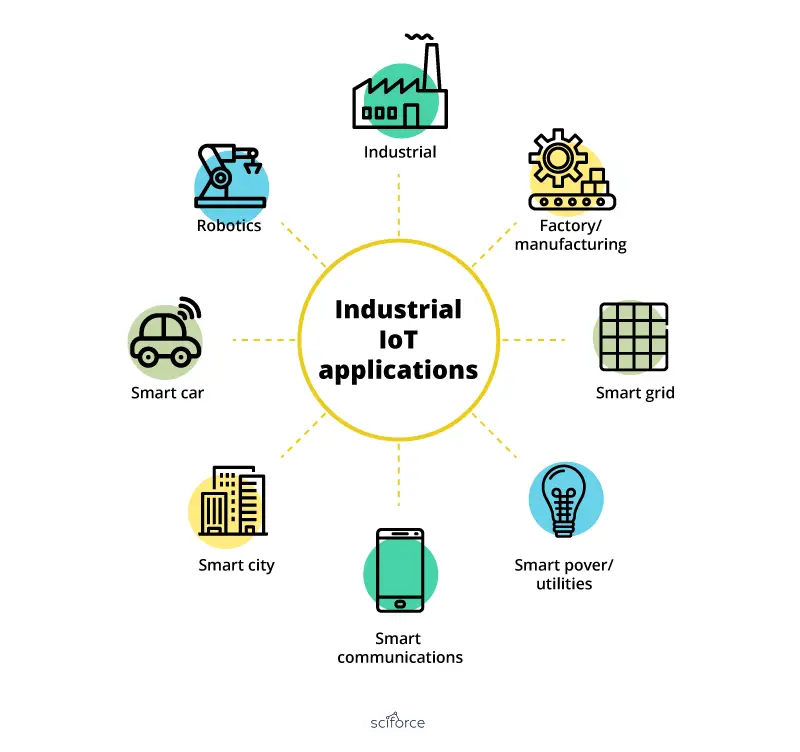
So, What exactly is IoT and how does it differs from IIOT? Well, the Internet of things (IoT) is the preparation of smart home devices. This allows us to connect the physical world to the digital world and thereby improving the overall consumer experience. A great example of this is your smart home appliances which can save a lot of electricity by turning themselves off automatically when you leave your home.
On the other hand, the Industrial IoT (IIoT) refers to the application of IoT in any industrial environment. People talk about a fourth industrial revolution or Industry 4.0. based on IoT technology. While IIoT relies on connected machinery, automation, and data collection and closes the gap between the digitization of business operations and their physical components in order to improve the efficiency of the industrial process.
IIoT is made up of more than just smart objects communicating with each other. There are users, machinery and applications in a constant interrelation, developed around an IoT platform and creating a private network. While IoT and IIoT have a lot in common, there are also aspects that make them different. The most important difference is made by how they make use of the same technologies.
The only difference between IoT and IIoT is the general use case. IoT focuses on increasing effectiveness, but also on improving the experience of users. For example, smart homes or wearables make performing daily tasks easier for all of us. On the other hand, IIoT is geared more towards improving the efficiency and performance of industrial activities and is less concerned with improving the quality of life for users. IoT is used by both consumers and professionals, while IIoT is used only by specialists in certain industrial areas.
Both IoT and IIoT are communication-based eco-system. They both have common concepts like data management connectivity, data security, and a secure cloud-based server. While IoT devices mostly depend on the presence of a mobile device in order to connect to smart home devices, IIoT deals with machine management systems in factories which led to the innovation of smart factory and predictive technology.
How IIoT Creates the Factories of the Future
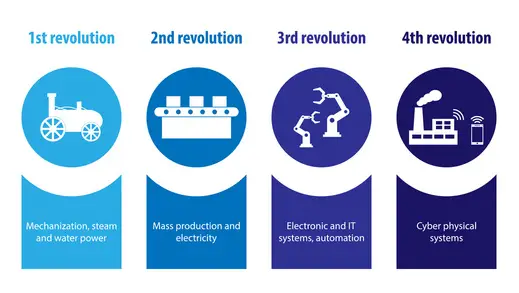
The technologies employed by the Industrial IoT are changing the way factories operate on every level. It has the potential to increase global productivity for up to 25% in the upcoming 5 years. The Internet of things for factories is a family of solution which combines the capabilities of analytics and smart computing to provide efficiency across the factory value chain. Industries like manufacturing are embracing the potential of IIoT while many production facilities are already using it. These technologies can be applied to all types of devices to ensure greater efficiency, increase productivity and improve health and safety on factory premises.
Smart Operations
Using smart technologies to connect machinery and systems that communicate with each other creates an interconnected factory environment. The data gathered by the sensors integrated into all these devices and equipment is stored in a central database. Plant Managers can better manage resources and improve worker expertise and provide a safe working environment by using the information provided by the data that was collected to obtain a better overall view of the factory’s functioning. They can analyze how certain parts of the system are performing and get all the relevant details to help them improve the process. From assembly lines to the resources that were used or the production level, everything can be monitored and possible flaws can be corrected.
Optimized Energy Use
One of the biggest issues in every industry is energy consumption. Factories are huge consumers and are constantly trying to find ways to reduce the amount of energy that is being used in the production process. IIoT gives managers a clear view of the energy consumption throughout the factory and provides them with details about how each specific piece of equipment uses energy. They can identify the devices that are inefficient and find ways to reduce energy waste, therefore reducing costs and environmental impact.
Improved Maintenance
Maintenance involves all the work put into keeping the machinery and equipment in proper functioning condition. While reactive maintenance means to fix a problem after it occurs, IIoT changes the game by focusing on predictive maintenance. The data collected through sensors offers detailed information about the state of each piece of machinery. The constant supervision of how devices perform enables workers to predict when an issue might arise and address it before it happens. This translates into reduced downtime and increased productivity.
The Benefits of IIoT
IIoT technology benefits the manufacturing industries in many different ways and can be integrated almost in every aspect of a business, bringing along positive changes and providing numerous benefits:
- Improved Efficiency: It helps the plants to get 100% efficiency out of their equipments. This is possible with the data that is constantly being collected in every system which can be used to manage and improve the functioning of each process. The detailed information that IIoT technologies offer the possibility to find solutions to a variety of problems and be one step ahead of the game by solving the issues before they cause any delay.
- Reduced Costs: Operational efficiency also means reducing expenses and producing maximum quality products. A good example is the smart use of energy and raw materials. Saving on these things can make a huge difference for any company’s budget.
- Remote Control: The IoT Sensors and other devices that are deployed across the factory and supply chain provide real-time actionable insights. Since all devices are connected to the internet, everything can be controlled remotely as long as there are a good internet connection and the necessary software.
- Better Customer Experience: IIoT allows manufacturers to understand how consumers use the products and services they provide and helps them identify the aspects that need improvement to enhance the customer experience.
- Business Innovation: IIoT also offers the possibility to develop innovative business models and create new revenue streams. Companies can use the data they possess to offer new services such as predictive maintenance.
The Challenges IIoT Faces
The many benefits of the IIoT can’t be denied. However, there are also challenges that must be taken into consideration when thinking about adopting the IIoT model. The company may very well understand, how important the IoT can be to their organization but they are struggling to achieve the liftoff.
While a number of organizations have already implemented the IoT, there is a large number that is still in the research and evaluation phases. So, why is it so difficult for manufacturers in adopting IoT? Well, the top challenges for manufacturers in adopting IoT are Security, Funding the Initial Investment, Privacy, Data Management, and Device Integration.
- Security: It is a significant concern for many companies since everything is connected to the internet runs the risk of being hacked. IIoT collects sensitive data through devices that most of the time have poor security features.
- Privacy: Another issue is the way private data are collected, used and stored. IIoT makes good use of the data it gathers, but it must do so while ensuring data privacy while ensuring others that the collected data is not a threat, it is just for their benefit.
- Data Management: Companies are faced with the challenge of managing a high volume of data collected by IIoT devices. Here factories manager has to give up their important asset which is intuition management and move on to data level management. These data must be first thoroughly analyzed before taking any action which is very challenging.
- Device Integration: IIoT comprises many different elements. Therefore, the IIoT system must integrate all these components in an effective manner in order to work at full potential.
Conclusion
The potential for smart factories is enormous, the IIOT and next-generation networking technologies have already brought the future of manufacturing. By combining machine to machine communication along with big data analytics IIoT has driven great results in areas such as efficiency, productivity, and performance.

