Back when the first three-wheeler and four-wheeler motor vehicles were invented in the 1800s, every stage of production was handled by humans. From assembling the cars themselves to taking care of the supply chain, procurement of raw materials, handling dealerships, and much more – there was a human behind everything. Shoot to 2021 to a pandemic-hit economy and we are now looking to reduce reliance on humans and shift them on to machines and robots to take care of almost everything.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a collective term that includes capabilities shown by computer systems that are perceived by humans as representing intelligence. In today’s world, typical AI capabilities include speech, image and video recognition, autonomous objects, natural language processing, conversational agents, prescriptive modeling, augmented creativity, smart automation, advanced simulation, as well as complex analytics and predictions.
Also read: How to Become an Artificial Intelligence Developer?
Companies such as Tesla are already automating most of the manufacturing process. In 2018, Tesla said that over 95% of its Model 3 production is automated. Ola, which is known for its cab services, has started its own vision of creating a fully automated two-wheeler mega factory that will have the capacity to manufacture a scooter in just 2 seconds!

But how did we get here and what’s next for Artificial Intelligence in this sector? Let’s check out some of the most popular use cases of AI and break them down to understand what the future holds.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Automotive Industry
AI has come quite far from its initial use of just navigation software to now fully autonomous driving. automated supply chains and more. As you can see from the snapshot of FutureBridge Analysis’s research below, the exhibits are broken down into three main sectors – Manufacturing, Transportation, and Service.
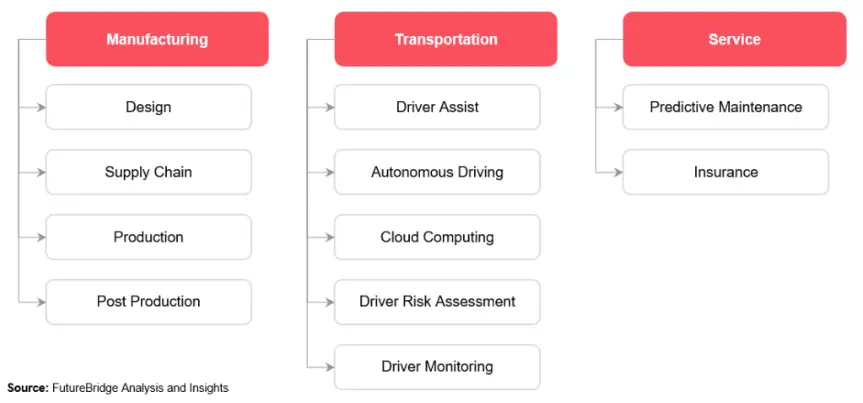
Manufacturing
The most noticeable change is the emergence of artificial intelligence in automotive manufacturing. Robots now work with humans and drive up the assembly line process in an efficient manner. AI-powered painting and welding are now standard across major automotive manufacturing factories. Not only do they automate the whole process, but can also identify defects in materials and alert quality control staff about it.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are also becoming common in the manufacturing sector. These vehicles are powered by AI and can identify loaded objects, adjust routes and deliver materials from one point to another.

Generative Design is also something that is making its presence felt in the automotive and industrial fields. One such example is BMW. The German car manufacturer is utilizing generative design techniques in fields including the design of new wheel rims and car seats for a wide variety of applications.
“We are feeding both technical parameters and design concepts into the program. It has the ability to learn and takes into account the different specifications as it creates variants,” says Holger Hampf, President of BMW subsidiary Designworks.
Artificial Intelligence also allows automating of supply chain processes like demand forecasting and production planning. These key processes have the potential to drive the manufacturing cost up or down, depending upon how streamlines the entire process actually is. This is why every company is working on AI solutions that can automate such contingencies.
Some of the things AI can do right now are –
- Calculate the space in a warehouse and recommend the best possible loading options for specific products.
- Semi-automate the process of checking in and loading cargo.
- Use cognitive visual recognition to check products before delivery.
These are just some of the number of use cases AI has in manufacturing and is likely to grow in the near future.
Transportation
The push for more assistive and auto machine learning features in vehicles has also pushed the growth of Artificial Intelligence in transportation. This is to ensure improved driving comfort and safety. Features such as lane assistance, adaptive cruise control, and automated parking are already being developed, tested, and offered on consumer vehicles.
Several companies are developing AI for consumer vehicles including Audi AG, Alphabet Inc., BMW, Daimler AG, Didi Chuxing, Ford Motor Co., General Motors, Harman International Industries, Honda Motor Co., IBM, Microsoft, Tesla, Uber Technologies, and Volvo Car Corp.

These giants primarily focus on long-term contracts and strategic partnerships to develop AI. Several next-gen sensors and onboard computers can classify various parameters like traffic, road infrastructure, and pedestrians.
This segment of context awareness will see a 35% annual growth between 2019 and 2026 and is based on high demand for semi-automated cruise control and driver-assistance features.
To keep up with the demand, tech companies are heavily investing in the development of innovative technologies. Intel has invested around $250 million into key technologies such as deep learning, connectivity, security, and other AI-related tech.
Not just tech companies but even governments are now investing to deploy AI in the auto industry. For instance, the UK Government has invested more than $75 million to improve mobility and AI solutions. The European Commission has also mandated rules that will make cars manufactured after 2021 have a built-in image or signal recognition. At the end of the day, the goal is to have a greater sense of on-road safety for both passengers and pedestrians alike.
Driver Monitoring features are also entering the market. Such software can tell whether a driver is in their vehicle and adjust the seat, mirrors, and even temperature depending upon the driver profile. The software can also detect the head position and monitor the driver’s eyes to detect drowsiness and wake up the driver in case of an emergency.
After Sales and Service
Remote AI can be used to “update” the firmware of cars over time. Tesla’s self driving feature gets regular over-the-air updates that improves the capabilities of the car. They collect data from hundreds of thousands of connected drivers, and use them to develop the software. This data includes trip info, telemetry, RPM engine, acceleration and deceleration, accidents and more.
This data can also be used for insurance purposes. Companies such as Nexar and TrueMotion are already using dashboard cameras, smartphone cameras, and other IoT sensors to detect the movement of vehicles. They can detect other objects on the road as well as heavy breaking when a car makes a sudden stop. All of this data can be affect insurance deductions or premiums and can be shared with companies.
Some software can also detect how much damage a car has incurred based on photos of it. After analysing the image, the software can then detect the severity of it and provide an initial repair cost. These telemetrics will ensure that the process is faster and more accurate.
Artificial Intelligence has also been making its way into marketing. According to a report from Capgemini, Volkswagen has been using Artificial Intelligence to predict sales of 250 car models in 120 countries.
The software also took into account other forms of data such as information on economic and political conditions as well as meteorological data. All in all, AI has proven to be useful after the customer has purchased a vehicle and will continue to do so, as we advance more into AI-powered tools and services.
What’s Next?
Artificial Intelligence is all set to see an unprecedented growth in the coming future, especially in the next decade. As technology makers are collaborating with OEMs, there is going to be a surge in use cases across the automotive industry. AI cannot really replace humans but can perform tasks that require scale, speed and accuracy better than us.
Comment down below your views about Artificial Intelligence in the automotive industry and whether or not you will enjoy going to work without having to worry about traffic lights or highway congestions.
